Advanced Scraping with Puppeteer: Techniques for Reliable, Scalable, and Stealthy Scrapers
Advanced Scraping with Puppeteer: Techniques for Reliable, Scalable, and Stealthy Scrapers
In the previous guide, we learned how to build a basic web scraper using Node.js and Puppeteer. We scraped quotes, handled pagination, and saved results into a file.
But real-world scraping often gets more complex:
- Websites detect and block bots.
- Captchas appear unexpectedly.
- Data loads asynchronously.
- Pages require user authentication.
- IPs get banned after too many requests.
In this advanced guide, we’ll dive deep into real-world challenges and learn powerful techniques to make your Puppeteer scrapers faster, stealthier, and more reliable.
We’ll cover:
- Headless browser detection & stealth mode
- Using proxies
- Handling captchas
- Managing sessions, cookies, and authentication
- Speed optimization techniques
- Running scrapers at scale
- Error recovery and retries
Let’s get into it! 🔥
1. Headless Browser Detection and Stealth Mode
Problem:
Websites can detect Puppeteer bots because browsers running in headless mode leave tell-tale signs:
- Missing plugins
navigator.webdriverset totrue- Strange screen resolutions or languages
Solution:
Use puppeteer-extra and puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth to make Puppeteer look like a real user.
Install stealth plugin:
npm install puppeteer-extra puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth
Modify your scraper:
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer-extra');
const StealthPlugin = require('puppeteer-extra-plugin-stealth');
puppeteer.use(StealthPlugin());
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({ headless: true });
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://bot.sannysoft.com'); // Tests bot detection
await page.screenshot({ path: 'stealth_test.png' });
await browser.close();
})();
🔹 Result: Your scraper now looks like a normal user browsing!
2. Using Proxies to Avoid IP Bans
Problem:
Sending 1000s of requests from the same IP address can trigger bans.
Solution:
Use proxies (rotating residential proxies, datacenter proxies, or even your own servers).
Using a proxy with Puppeteer:
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
args: ['--proxy-server=http://username:password@proxyserver:port']
});
Example:
args: ['--proxy-server=http://123.45.67.89:8080']
If your proxy requires authentication:
await page.authenticate({
username: 'your-username',
password: 'your-password'
});
Proxy Rotation (Simple Example):
If you have multiple proxies:
const proxies = [
'http://user:pass@proxy1:port',
'http://user:pass@proxy2:port',
'http://user:pass@proxy3:port'
];
const randomProxy = proxies[Math.floor(Math.random() * proxies.length)];
const browser = await puppeteer.launch({
args: [`--proxy-server=${randomProxy}`]
});
🔹 Tip: Services like BrightData, Oxylabs, or Smartproxy offer thousands of rotating IPs.
3. Handling Captchas Automatically
Problem:
Captcha challenges can stop your scrapers.
Solution:
You can either:
- Solve simple captchas with image recognition (hard!).
- Use external solving services like 2Captcha or AntiCaptcha.
Example using 2Captcha:
Install 2captcha npm package:
npm install 2captcha
Solve a captcha:
const solver = require('2captcha')('YOUR_2CAPTCHA_API_KEY');
solver.solveImage('captcha.png').then(
(text) => console.log('Captcha text:', text),
(err) => console.error('Error:', err)
);
You can take a screenshot of the captcha in Puppeteer and send it to the solver!
(Optional) ReCaptcha Solver Plugin for Puppeteer:
npm install puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha
const RecaptchaPlugin = require('puppeteer-extra-plugin-recaptcha');
puppeteer.use(
RecaptchaPlugin({
provider: {
id: '2captcha',
token: 'YOUR_2CAPTCHA_API_KEY'
},
visualFeedback: true
})
);
await page.solveRecaptchas();
🔹 Result: Your scraper bypasses ReCaptcha v2 automatically!
4. Managing Sessions, Cookies, and Authentication
Problem:
Many sites require login before scraping.
Solution:
Simulate logging in and save your session cookies for later use.
Example: Login and save cookies:
await page.goto('https://example.com/login');
await page.type('#email', 'your-email@example.com');
await page.type('#password', 'your-password');
await page.click('#submit');
await page.waitForNavigation();
const cookies = await page.cookies();
fs.writeFileSync('cookies.json', JSON.stringify(cookies, null, 2));
Later, reuse cookies:
const cookies = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('cookies.json'));
await page.setCookie(...cookies);
await page.goto('https://example.com/dashboard');
🔹 Result: No need to log in every time! Saves time and reduces load.
5. Speed Optimization Techniques
Problem:
Scraping large websites is slow.
Solutions:
- Disable images, stylesheets, fonts
- Set fast timeout settings
- Use parallel browsers
Block unnecessary requests:
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
page.on('request', (req) => {
if (['stylesheet', 'font', 'image'].includes(req.resourceType())) {
req.abort();
} else {
req.continue();
}
});
🔹 Result: 2-5x faster scraping!
Increase parallelism:
Instead of scraping pages sequentially, run multiple browser instances:
Promise.all([
scrapePage('https://site.com/page1'),
scrapePage('https://site.com/page2'),
scrapePage('https://site.com/page3')
]);
(But beware of overloading the target website!)
6. Error Recovery and Retry Mechanisms
Problem:
Web pages sometimes fail to load, elements are missing, or network issues occur.
Solution:
Use retry logic.
Retry wrapper example:
async function retryRequest(page, url, retries = 3) {
for (let i = 0; i < retries; i++) {
try {
await page.goto(url, { waitUntil: 'domcontentloaded', timeout: 30000 });
return;
} catch (error) {
console.error(`Failed attempt ${i + 1} for ${url}`);
if (i === retries - 1) throw error;
await new Promise(res => setTimeout(res, 2000));
}
}
}
🔹 Result: More stable scrapers that survive temporary issues.
7. Running Scrapers at Scale
Once your scraper works reliably, you might want to scale to hundreds of thousands of pages!
Some tools and techniques:
- Cluster Management: Use
puppeteer-clusterfor automatic job distribution. - Docker Containers: Deploy scrapers as lightweight containers.
- Headless Chrome Servers: Run multiple headless browsers on cloud servers.
- Queue Systems: Use Redis or RabbitMQ to manage scraping queues.
Bonus: Puppeteer-Cluster Example
puppeteer-cluster allows running many pages in parallel without manual thread management!
Install:
npm install puppeteer-cluster
Example:
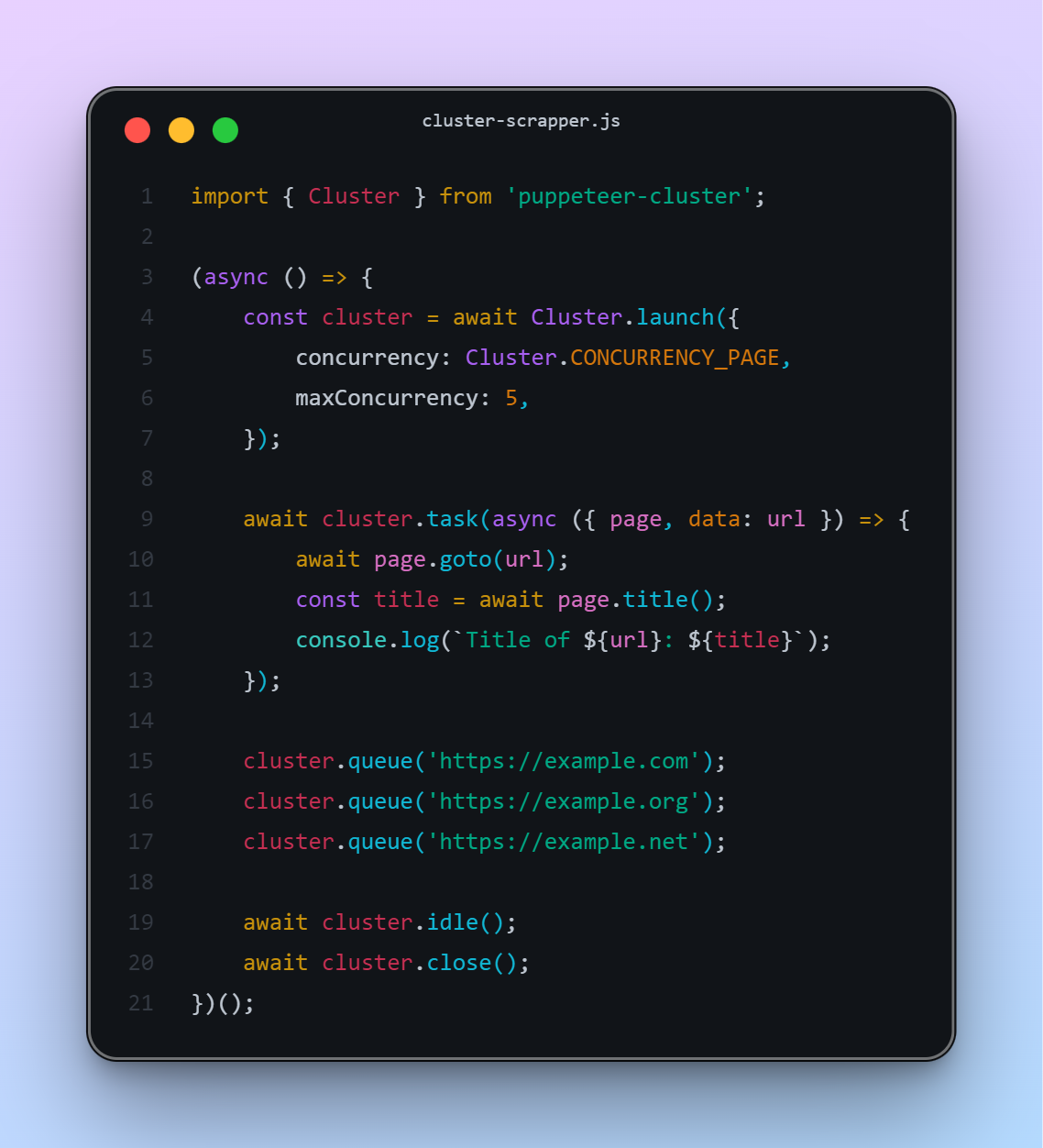
🔹 Result: Efficient, concurrent scraping at scale!
Final Thoughts
Building advanced web scrapers with Puppeteer unlocks incredible possibilities:
- Competitive analysis
- Price monitoring
- SEO research
- Market intelligence
- Academic data gathering
- Automation of boring tasks
But remember:
✅ Always scrape ethically
✅ Respect site rate limits
✅ Use stealth and proxy techniques carefully
✅ Monitor and log errors
✅ Build robust retry mechanisms
Happy scraping! 🚀
Leave a comment